Secure a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Understanding the Nasal Flare Area for Botox Treatment
The nasal flare area, also known as the lateral canthi, refers to the region just below the outer corner of the nose, where the nostrils meet. This area is a common site for botulinum toxin (Botox) injections when treating conditions such as excessive sweating, frowning, and eye twitching.
Nasolabial folds are deep lines that originate from the nasal tip and extend downwards to the mouth, creating a “smile line”. These folds can make the face appear older than it truly is, contributing to a worn-out or tired appearance. Botox injections can effectively relax the muscles causing nasolabial folds, resulting in smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
When performing Botox treatments on the nasal flare area, it’s essential to consider the anatomy of the face and surrounding structures. The area is surrounded by sensitive nerves, blood vessels, and cartilage, which must be carefully avoided during injection to minimize potential side effects.
Naso-labial fold injections are typically placed in the following areas:
- Just lateral to the nasal alar rim (the curved edge of the nostril)
- Around the lateral canthal tendon (the area where the eyelid meets the nose)
- In the skin just above the nasolabial fold, in a perpendicular plane
Botox injections are usually performed using a fine-gauge needle and a small amount of Botox solution. The injection process typically takes only a few seconds to complete, and patients often report minimal discomfort or no sensation at all.
It’s crucial to note that the nasal flare area should not be treated with Botox for conditions such as excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) or nasal congestion, as this can lead to adverse effects like nose asymmetry or breathing difficulties.
Naso-labial fold injections are considered a highly effective treatment for reducing nasolabial folds and promoting facial rejuvenation. When performed by an experienced healthcare professional, Botox treatments in the nasal flare area can provide remarkable results, effectively minimizing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and restoring a smoother, more youthful complexion.
The Nasal Flare Area, also known as the glabellar area, is a critical region for individuals seeking Botox treatment to reduce excessive blinking, nasal flaring, or forehead movements.
This area is located on the bridge of the nose, specifically between the eyebrows and the sides of the nose.
To effectively target the muscles responsible for nasal flaring, H2 units (a type of neurotoxin) are strategically placed in this area to relax the overactive muscles that cause excessive movement or twitching.
The glabellar muscle complex, which includes the procerus, orbicularis oculi, and corrugator supercilii muscles, plays a significant role in nasal flaring
When these muscles are activated, they can cause the nose to flare or puff out, resulting in an unpleasant appearance.
By injecting H2 units into the nasal bridge, it is possible to relax these overactive muscles and reduce or eliminate nasal flaring.
The placement of H2 units in this area requires a deep understanding of facial anatomy and muscle structure, as well as excellent technique to avoid unwanted side effects or complications.
Experienced healthcare professionals will use a combination of ultrasound guidance, facial mapping, and anatomical knowledge to precisely target the muscles responsible for nasal flaring.
This targeted approach ensures that only the necessary amount of H2 units is injected into the correct area, minimizing the risk of over-treatment or uneven distribution.
After treatment, patients can expect a significant reduction in nasal flaring, resulting in a more aesthetically pleasing and relaxed appearance.
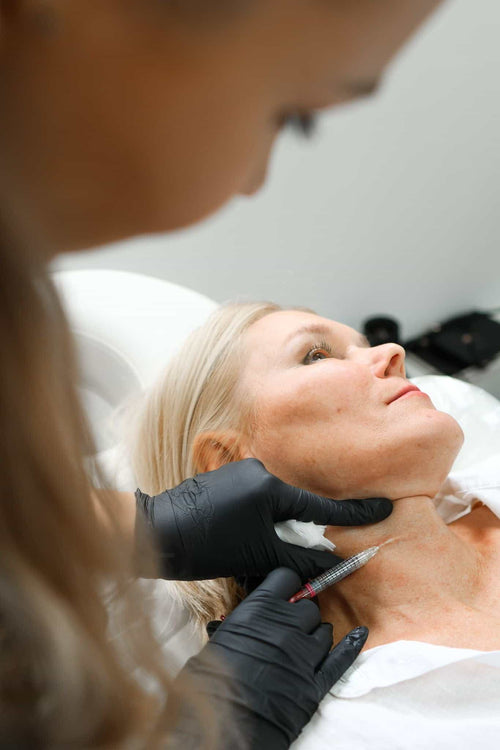
The effectiveness of Botox in the Nasal Flare Area can vary from individual to individual, depending on factors such as muscle tone, facial structure, and treatment goals.
However, with proper technique and a deep understanding of facial anatomy, H2 units placed in the nasal bridge can provide long-lasting results and a more refined appearance.
It’s essential to consult with an experienced healthcare professional who specializes in Botox treatments to determine if this area is suitable for treatment and to discuss individualized treatment options.
The Nasal Flare Area (NFA) refers to a specific region on the nose, specifically the area between the nostrils and the bridge of the nose. This area is targeted for Botox treatment due to its connection with the nasolabial fold, which is often responsible for the flare.
The nasolabial fold is the crease that runs from the nose to the mouth, connecting it to the lateral canthus (the outer corner of the eye). When the nasolabial fold becomes too prominent or deepens, it can cause a nasal flare, which is characterized by a widening of the nostrils and a more pronounced curvature of the nose.
Botox injections in the NFA are designed to relax the orbicularis oculi muscle (the muscle around the eye) and the zygomaticus major muscle (the muscle that raises the corner of the mouth), as well as other nearby muscles, including those in the nasal area. By relaxing these muscles, Botox can help to soften and reduce the appearance of the nasolabial fold, thereby minimizing the nasal flare.
The NFA is a relatively small area, but it requires precise placement of the Botox injections. The goal is to target the specific muscles responsible for the nasolabial fold and the nasal flare, while avoiding nearby areas that may not require treatment.
Here are some key points about where nasal flare Botox is placed:
- Distal orbicularis oculi muscle: This muscle runs from the orbital rim to the nose and plays a role in the formation of the nasolabial fold. Botox injections here can help relax this muscle and reduce the appearance of the nasolabial fold.
- Medial orbicularis oculi muscle: This muscle runs from the orbital rim to the nasal bone and also contributes to the formation of the nasolabial fold. Botox injections here can help relax this muscle as well.
- Zygomaticus major muscle: This muscle runs from the cheekbone to the nose and plays a role in the formation of the nasolabial fold. Botox injections here can help relax this muscle and reduce the appearance of the nasolabial fold.
- Nasalis muscles: These small muscles run from the nasal bone to the nostrils and contribute to the shape and movement of the nose. Botox injections here can help relax these muscles and reduce the appearance of the nasal flare.
It’s worth noting that the specific placement of the Botox injections may vary depending on the individual’s anatomy and the extent of the nasolabial fold and nasal flare. A qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist will be able to assess the area and determine the best course of treatment.
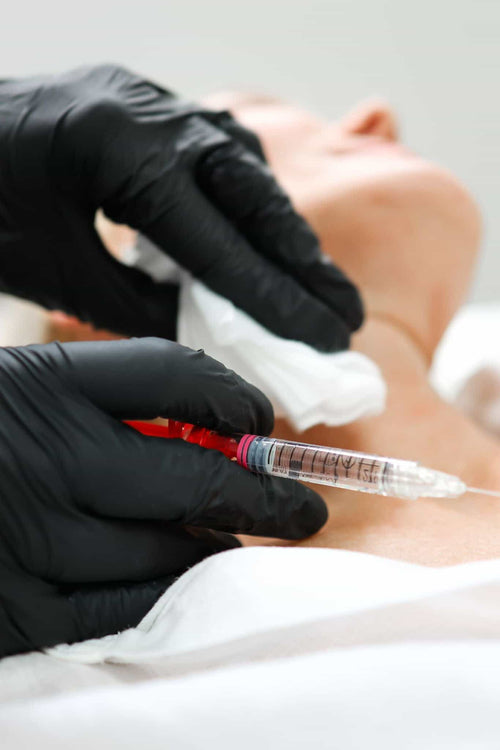
Specific Placement Details
The specific placement details for nasal flare Botox injections are crucial for effective and safe treatment.
In general, the goal of Botox injections for nasal flare is to temporarily relax the muscles that cause the nose to flare or become wider.
Nasal flaring typically involves two main muscle groups: the procerus and orbicularis oculi muscles.
The procerus muscle is located between the nose and the bridge of the nose, and it helps to bring the nose towards the bridge when it contracts.
The orbicularis oculi muscle is responsible for closing the eyelid and is also involved in nasal flaring, particularly on the lateral (outer) aspect of the nose.
For Botox injections aimed at reducing nasal flare, a total of 2-4 units are typically injected into each of these muscles, depending on individual factors such as muscle size and desired effect.
Specifically, the procerus muscle receives an injection along its midline, usually about 1-2 mm from the nose tip, with a slight deviation towards the bridge.
The orbicularis oculi muscle is injected slightly laterally to the nostril, approximately at the level of the nose’s nasolabial fold.
It’s essential for the injector to be aware that the nasal flaring effect can vary depending on factors such as facial anatomy and emotional expressions.
Additionally, Botox injections should not be administered too close to the nostrils themselves, as this may cause irritation or other complications.
The ideal distance between the Botox injection site and the nostril is typically at least 3-4 mm to minimize risks.
It’s also worth noting that nasal flare Botox injections should only be administered by an experienced healthcare professional with extensive training in facial anatomy and botulinum toxin injection techniques.
Nasal flare, also known as nasal tip ptosis or nasal asymmetry, is a common concern for many individuals seeking Botox injections. To minimize risks and achieve optimal results, it’s essential to understand where nasal flare Botox injections are typically placed.
The primary goal of Botox injections in treating nasal flare is to temporarily relax the muscles that cause the nostrils to flare outward. To achieve this, Botox is administered around the nasal artery and vein.
- **Nasal Artery:** The nasal artery runs along the lateral wall of the nose and supplies oxygenated blood to the nasal tissues. Injections are typically placed near the artery to ensure effective relaxation of the surrounding muscles.
- **Nasal Vein:** The nasal vein also plays a crucial role in nasal flare. Botox injections may be placed nearby to relax the muscle that compresses this vein, reducing its diameter and minimizing swelling or bruising.
- **Periorbital Muscles:** To maintain facial balance and symmetry, Botox injections may also be administered around the periorbital muscles (the muscles surrounding the eyes). These injections help relax the procerus and orbicularis oculi muscles, which contribute to nasal flare.
- **Mons Terminus Muscles:** The mons teres muscle, located at the base of the nose, also plays a significant role in nasal flare. Botox injections may be placed near this muscle to relax its contraction and reduce nostril flaring.
The optimal placement of Botox injections for nasal flare depends on individual anatomy and the specific muscle imbalances present. A qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist will assess the patient’s unique needs and tailor the treatment plan accordingly.
Accurate placement of Botox injections is crucial to achieve effective results while minimizing risks, such as bruising, swelling, or infection. With proper technique and attention to detail, Botox injections can be an effective treatment for nasal flare, providing a smooth, even appearance that enhances facial balance and harmony.
Nasal flare, also known as nasal lift or nasal contouring, is a cosmetic procedure that involves injecting Botulinum toxin (Botox) into specific areas of the nose to improve its shape and appearance.
According to Harvard Health Publishing, the structures most susceptible to damage during injection in this area are the nasal septum, the turbinate bones, and the nasal cartilage.
The nasal septum is a thin wall of cartilage and bone that separates the two sides of the nose. It is located in the middle of the nose and contains the nasal passages. The septum can be delicate and may require extra care when injecting Botox to avoid damaging it.
The turbinate bones are small, cone-shaped bones that are embedded within the nasal cavity. They help to warm, humidify, and filter the air we breathe. However, they are also quite fragile and can easily be damaged during injection.
Nasal cartilage is a flexible, yet strong, connective tissue that provides structural support to the nose. There are several types of nasal cartilage, including the alar cartilages, which make up the upper part of the nostrils, and the septal cartilage, which forms the bridge of the nose.
During a nasal flare procedure, Botox is typically injected into the following areas:
– The lateral canthal tendon: This is a tendinous structure that runs from the inner corner of the eye to the eyelid. Injecting Botox into this area helps to pull back the corner of the eye and widen the nostrils.
– The nasal alar rim: This is the outer edge of the nostril. Injecting Botox into this area helps to lift the tip of the nose and create a more defined shape.
– The levator labii superioris muscle: This muscle runs from the upper lip to the nasal bone and helps to elevate the upper lip and the bridge of the nose. Injecting Botox into this area helps to reduce the size of the nose and create a more balanced appearance.
It’s worth noting that not all patients are suitable for nasal flare surgery, especially those with certain medical conditions or taking certain medications. Patients should consult with a qualified healthcare professional or plastic surgeon to determine if nasal flare is right for them.
Precautions and Considerations
Nasal flaring is a common issue that can be treated with Botox injections. When determining the placement of these injections, it’s essential to consider the anatomy of the nose and the surrounding areas.
The nasal flaring area typically involves the nasal lateral cartilages and the nasal septum. However, to avoid causing any damage or complications, a careful evaluation of the area is necessary.
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
One crucial consideration when placing Botox injections for nasal flaring is avoiding the medial cannthal ligament. This ligament connects the medial canthus (the inner corner of the eye) to the lateral canthus and plays a significant role in maintaining eye shape and alignment.
Another critical area to avoid is the nasojugal fold, also known as the nasolabial fold or the glabella. This fold runs from the nose to the mouth and contains vital nerves and blood vessels that need to be protected during Botox injections.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider the nasal septum, particularly the area around the cribriform plate. This region is rich in blood vessels and nerves, making it a sensitive area for injection.
The nasal turbinates, also known as the ethmoidal air cells, should also be avoided during Botox injections for nasal flaring. These structures can be easily damaged, leading to breathing difficulties or other complications.
A thorough evaluation of the nasal anatomy and surrounding areas is crucial before administering Botox injections for nasal flaring. This helps ensure that the treatment is effective while minimizing the risk of complications or adverse effects.
The placement of Botox injections should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional with experience in administering these treatments. It’s also essential to carefully assess each patient’s individual anatomy and medical history before proceeding with treatment.
Nasal flare Botox injections are typically administered to reduce the appearance of nasal protractors, which are muscles that cause the nose to flare out when breathing in. However, plastic surgeons often advise taking certain precautions and considerations when placing Botox in this area.
One key consideration is avoiding placement near the nasal septum, a thin wall of cartilage and bone that separates the two sides of the nasal passages. The nasal septum is a sensitive area, and injecting Botox too close to it can cause irritation, bleeding, or other complications.
Plastic surgeons also recommend avoiding placement within one centimeter of the nostrils, as this area is highly sensitive and may be more prone to bruising or swelling. Injecting Botox too close to the nostrils can also increase the risk of nasal congestion or breathing difficulties.
Another important consideration is the depth of injection. The goal of nasal flare Botox injections is to relax the muscles that cause the nose to flare out, rather than injecting the toxin deep into the nasal septum or sinus tissue. Plastic surgeons often use a shallow injection technique to minimize the risk of complications and maximize the effectiveness of the treatment.
It’s also worth noting that some individuals may be more susceptible to complications from nasal flare Botox injections. For example, people with bleeding disorders or those taking certain medications may be at higher risk of bruising or other side effects. It’s essential for patients to discuss their individual risks and benefits with a qualified plastic surgeon before undergoing treatment.
Finally, it’s crucial for patients to follow post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications. This includes avoiding strenuous activities, rubbing or touching the treated area, and using ice packs to reduce swelling and bruising.
In addition to these precautions, plastic surgeons may also use various techniques to ensure safe and effective placement of nasal flare Botox. For example, they may use a topical anesthetic cream or spray before injection to minimize discomfort, or employ a specific injection technique that targets the muscles responsible for nasal protraction.
Nasal flap or nasal sidewall injections are a common technique for administering Botox to the nasal area.
The University of California, San Francisco Medical Center emphasizes the importance of taking precautions when performing nasal Botox injections to prevent complications such as dryness, crusting, or even nasal septal perforation.
One crucial consideration is the anatomy of the nasal cavity, particularly the nasal turbinates and the nasolabial folds. It’s essential for healthcare professionals to understand the spatial relationships between these structures to avoid injecting Botox into sensitive areas.
The ideal location for Botox injections in the nasal area is typically at a 45-degree angle, using a small cannula or needle. This allows for precise placement and minimizes the risk of accidental injection into surrounding tissues.
Another consideration is the amount of Botox used. The typical dose range for nasal Botox is between 10-20 units, depending on the individual’s anatomy and desired effects.
Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Your Dermal Fillers Now
It’s also essential to note that nasal Botox injections should be performed by a trained healthcare professional with experience in facial aesthetics and nasal anatomy.
A thorough patient consultation is necessary to discuss the risks and benefits of Botox injections in the nasal area, as well as to assess individual suitability for treatment.
Additional precautions may include using topical anesthetics or numbing agents to minimize discomfort during injection, as well as employing techniques to reduce bleeding and swelling.
Adequate post-injection care is also vital to prevent complications. Patients should be advised on how to manage potential side effects such as dryness, crusting, or nasal congestion.
It’s essential for healthcare professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest research and guidelines on nasal Botox injections to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Furthermore, patients should be informed about potential contraindications, such as facial paralysis, eye problems, or allergies, and any other underlying medical conditions that may affect treatment outcomes.
By taking a careful and nuanced approach to nasal Botox injections, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of complications and achieve optimal results for patients seeking facial rejuvenation treatments.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of nasal anatomy, Botox pharmacology, and patient-specific factors is necessary for safe and effective treatment of nasal area with Botox.
Read more about Live Your Vows here. Read more about Classy Pleasure here. Read more about Line the Studio here. Read more about Crimson Hill here.
- Juvederm Volite Skin Booster Treatments Near Englefield Green, Surrey - December 23, 2024
- Neauvia Hydro Deluxe Skin Booster Treatments Near Laleham, Surrey - December 22, 2024
- Jalupro Super Hydro Skin Booster Treatments Near Shere, Surrey - December 20, 2024
